In this post, we briefly discuss the architecture behind the React Native framework, giving a high-level overview of what makes it go.
Let’s take a look at one screen from an app that is purely React Native and ask ourselves what is the UI that we see here.
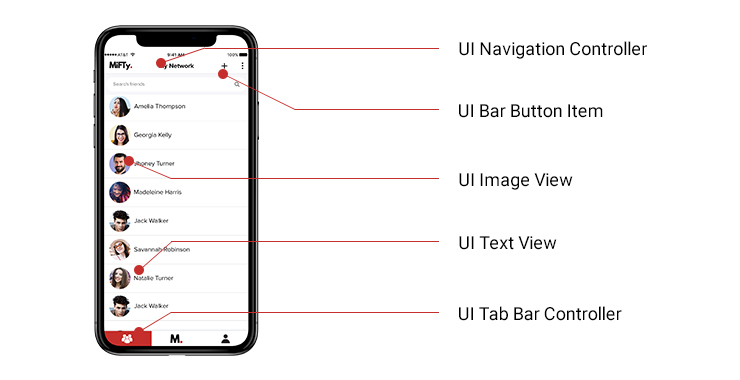
Is this HTML? Is this a webview like other implementations in PhoneGap or Cordova?
The answer is, without a doubt, no. The views
in React Native are purely native views so, from our app, the navigation
controller that you see here at the top bar is the
UINavigationController. Now, if you are an iOS developer, you would see
these are the same UI views that you use in your native apps.
 If
I had shown you the same screen on Android, you would see that the
implementation is completely different. It renders to the native views.
If the UI is completely native with React Native, where is the
JavaScript?
If
I had shown you the same screen on Android, you would see that the
implementation is completely different. It renders to the native views.
If the UI is completely native with React Native, where is the
JavaScript? Where Is the JavaScript?
JavaScript is what running under the hood. Where you as a
developer specify the business logic and which components you want, and
then the framework renders it for you. To understand this better, let's
dive into React Native a little deeper and see the architecture from the
inside.
Understanding React Native Architecture
Consider that there are two realms running side-by-side in
your app. You have the JavaScript realm and you have the native realm.
JavaScript Realm
The JavaScript realm is where you program in JavaScript,
naturally. The code there is running on a JavaScript engine.
Specifically, React Native uses jscore, an open source JavaScript engine
for WebKit. You are probably familiar with other engines like V8. They
do the same things and this engine is running inside your app on one of
the threads. Your app is a process that has several threads in it.
JavaScript is just one of them.
Native Realm
In the native realm, you still develop in Objective-C and/or
Swift if you are on iOS or with Java if you are on Android. You use the
native, platform-specific languages that you used before and you have
the main UI thread as usual. In all platforms, you can usually change
the UI only from the main UI thread and you can create as many
background threads as you want.
The Bridge
These two realms are different and connecting these two
realms is the bridge. React Native is a very important construct in this
entire setup. Did you ever try to debug a React Native application
using Chrome, for example? So, when you debug a React Native application
using Chrome, then you have the two realms actually running on
different computers. You can run the JavaScript role entirely inside
Chrome itself. You can debug it inside the Chrome debugger and you have
the native realm still running on your phone. Then, instead of going
inside your app, you would go through a WebSocket. The bridge, which is
just a communication protocol, can travel over WebSocket as well.