Source: https://dzone.com/articles/hyperledger-vs-quorum-vs-corda-which-is-correct-fo
May. 07, 21 · Security Zone · Opinion
Hyperledger, Quorum, and Corda all are private, permissioned blockchains, meaning that network participation is restricted and not anyone can be part of the blockchain.
In our primitive blogs, we learned about the basics of Blockchain Technology, what are public and private blockchains. We understood the details of public blockchains like Bitcoin, Ethereum as well as private blockchains Hyperledger Fabric and Hyperledger Fabric 2, the private blockchains of the Hyperledger family. While each blockchain has its own features and advantages, not everything can be applied and implemented for a particular project or business. Every business has its own set of requirements, the challenges or problems vary from business to business and a lot of other factors like budget, infrastructure, resources, time, etc., have to be taken into account while choosing the right technology for a business project.
In the case of Blockchain, a business, depending upon its nature and functionality may require to choose either a public, a private or a hybrid blockchain. While one of our previous blogs explained the difference between Bitcoin and Ethereum, the public blockchains; this blog will shed more light on the difference between Hyperledger vs. Quorum vs. Corda, the private blockchains. Check below for Hyperledger vs. Quorum vs. Corda activity protocols over the years.
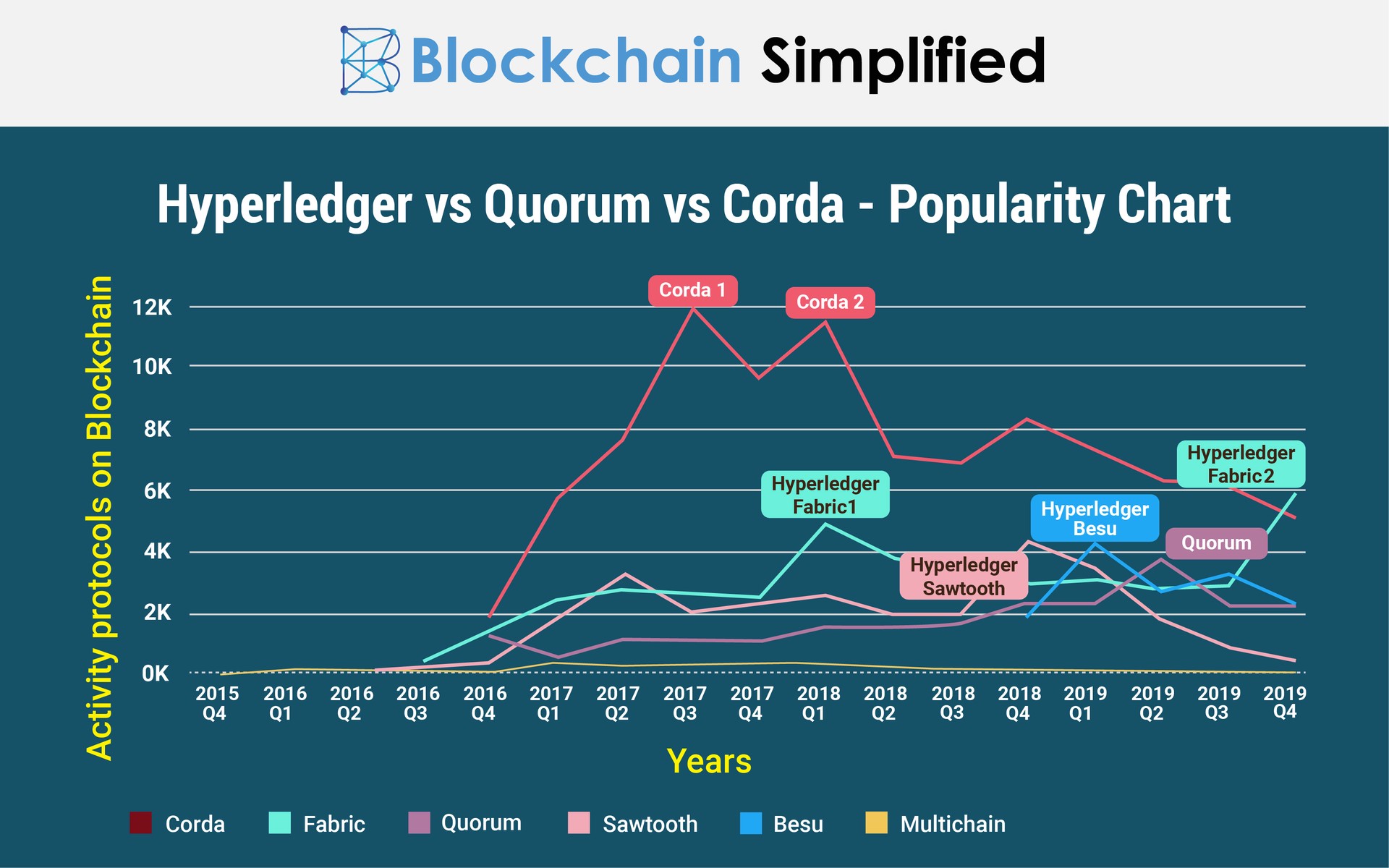
Hyperledger vs. Quorum vs. Corda
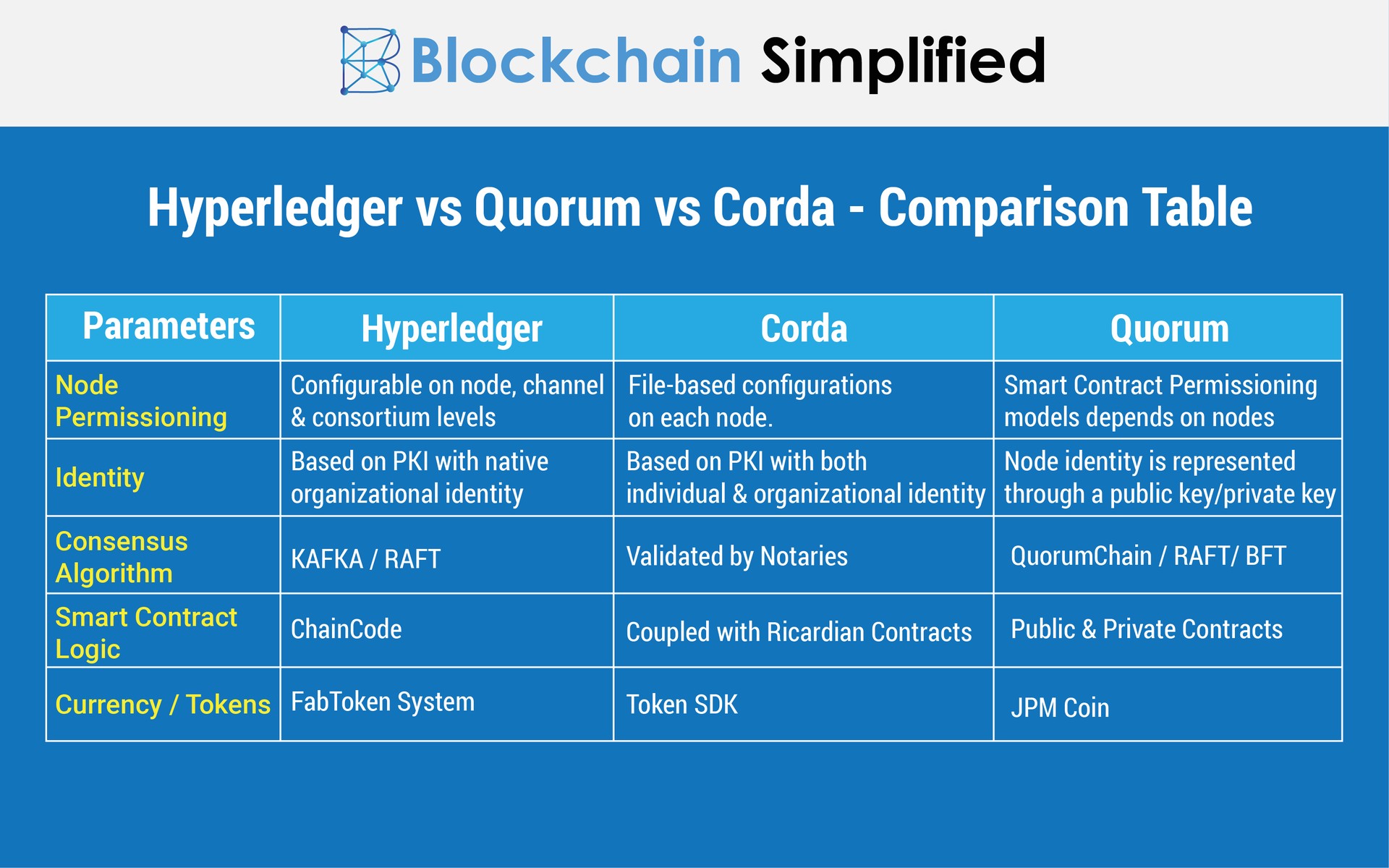
Node Permissioning
Hyperledger, Quorum, and Corda all are private, permissioned blockchains, meaning that participation in the network is restricted and not anyone can be part of the blockchain. A governing entity (typically a set of participants) allows the entry of participants in the blockchain and also decides the permissions of the other nodes/peers.
So in Hyperledger, the governing peers allow and provide permission to other nodes for any sort of transaction. This type of access control can be done on a node, channel, or even consortium level. Read more about Hyperledger node permissions in this article.
Corda has file-based configurations to access nodes and their permissions. Contrary to other blockchains, in Corda, data is shared only on a need-to-know basis instead of global broadcasts. Learn how nodes interact with others in Corda in this article.
Whereas in Quorum, node permissioning is specified in smart contracts. In technical words, a json file containing a permission flag is maintained for it. Read more about node permissioning in Quorum.
Consensus Algorithm
In the case of Hyperledger, rather than the sequential execution of transactions, multiple transactions can be executed simultaneously which enhances the performance of the system. For transactions to be executed and affirmed, Hyperledger follows the KAFKA and the RAFT algorithms to arrive at a consensus.
Corda was designed to especially serve banks and financial institutions and overcome challenges faced by this particular field. Hence, Corda coined the “Notaries” concept wherein the notaries validate the transactions and add blocks to the chain. Go through this documentation to know about Corda Notaries.
Quorum uses a protocol called the QuorumChain to reach consensus. A simple voting process that confirms transactions using the majority coupled with BFT and RAFT algorithms is used by this blockchain.
Smart Contract Logic
Hyperledger uses the Chaincode as its business logic. Chaincode can be written in any standard programming language like Node.js, Go, and Java.
As said above, Corda was developed for banks and financial institutes which emphasizes the need for a legal agreement between participants. Thus, Corda implements smart contracts coupled with Ricardian contracts to obtain validity and security. For Corda, the smart contract can be written using Java or Kotlin programming languages.
Quorum supports both public and private contracts which are written in Solidity programming language.
Currency/Tokens
Hyperledger facilitates the creation of native currencies as well as digital tokens using the FabToken management system.
Corda offers an SDK that allows the development of native tokens, issuance, and trading of the tokens.
The JPM coin is the digital currency of the Quorum Blockchain.
Conclusion
Enterprise blockchains are hugely popular and are much in demand for their scalable and adaptable characteristics. Hyperledger, Corda, and Quorum all offer privacy, robust mechanisms, scalability, and enhance blockchain performance. While Corda and Quorum have simple architecture, Hyperledger is more modular. Hence, it is up to organizations to decide which blockchain is more suitable and can be altered to their business needs.