Source: https://dzone.com/articles/natural-language-processing-1
Natural Language Processing is a sub-area of computer
science, information engineering, and Artificial Intelligence concerned
with the interactions between computers and human (native) languages.
This is nothing but how to program computers to process and analyze
large amounts of natural language data.
Natural Language Processing(NLP) = Computer Science + AI + Computational Linguistics
In another way, Natural Language Processing is the capability
of a computer software to understand human language as it is spoken.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is one of the components of Artificial
Intelligence (AI).
The real-life examples of natural language processing are
like understanding complete sentences, understanding synonyms of
matching words, speech recognition, speech translation, and writing
complete, grammatically correct sentences and paragraphs.
The applications of Natural Language Processing in various fields are as follows:
A) Machine Translation
The amount of information available is growing over the
internet. Machine translation helps us conquer language barriers that we
often encounter by translating technical manuals, support content or
catalogs at a reduced cost. The main challenge with machine translation
technologies is not in translating words, but in understanding the
meaning of sentences to provide an accurate translation.
B) Automatic Summarization
It reduces a larger text into a shorter, yet richly
constituted an abbreviated narrative representation of the original
document. It extracts keywords or key-phrases from a large piece of
writing. It creates an abstract of an entire article. Information
overload is a real problem when we need to access a specific, important
piece of information from a vast knowledge dataset. Automatic
summarization is important not only for summarizing the meaning of
documents and information but also to understanding the emotional
meanings inside the data, like in collecting information or data from
social websites. Automatic summarization mainly useful when used to
provide a summary of a news item or blog posts by avoiding repetition
from multiple websites and maximizing the dissimilarities of content
that obtained.
C) Sentiment Analysis

The aim of sentiment analysis is to identify sentiment among
several posts or even in the same position where emotion is not always
explicitly expressed. Many multinational companies are using natural
language processing applications, such as sentiment analysis, to detect
the opinions and sentiment over the internet to help them understand
what customers think about their products and services (i.e., “I love
the new mobile phones iPhone” and, after few lines “But many times it
won’t work well” where the person is still talking about the iPhone
mobile phones) and complete indicators of their reputation. Beyond
determining simple polarity, sentiment analysis understands the
sentiment in context to help you better understand what’s behind an
expressed opinion, which can be extremely relevant in understanding and
driving purchasing decisions. It is used to support the companies to
analyze a large number of reviews on a product. Also, it is used to help
the customer’s process the reviews provided on a product.
D) Document or Text Classification
Document or Text classification makes it possible to assign
predefined categories to a document and organize it to help you find the
information you need or simplify some activities. For example, an
application of text categorization is spam filtering in an email.
E) Speech Processing
- Text to speech: it converts electronic text to digital speech which is helpful for the deaf and dumb society
- Speech to text: it converts digital speech to text.
- Automatic Speech Recognition: Automatic transcription of spoken content to electronic text
- Speech to speech translation: Translating spoken content from one language to another in real time or offline.
F) Image Captioning
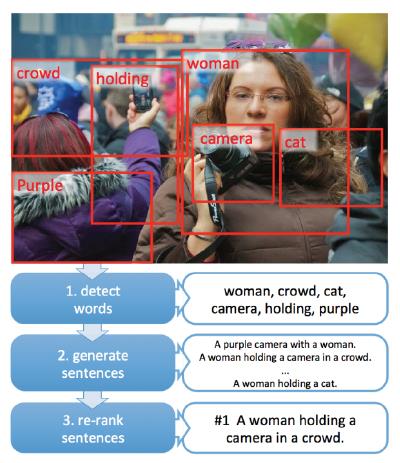
Image Captioning is a process of generating a textual
description of an image. It uses both Natural Language Processing and
Computer Vision to produce the captions.
G) Information Extraction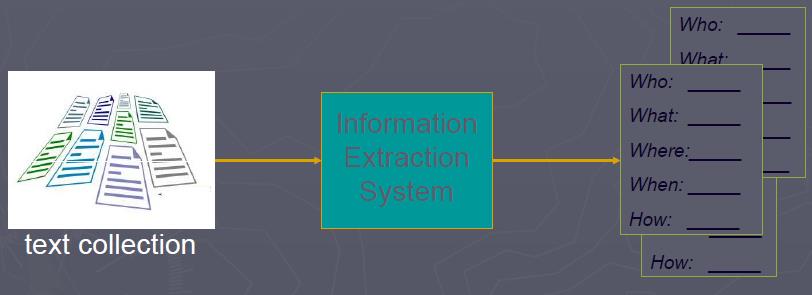
Information extraction is the way of obtaining a system
resource related to an information need from a collection of information
resources. The searches can be based on full-text or other
content-based indexing. Information extraction is the science of
searching for information in a document, searching for documents
themselves, and also searching for metadata that describes data, and for
databases of texts, images or sounds.
Extraction of Meaning From an Email:
I have decided to meet tomorrow at 10:00 am in the lab.
What to do: meeting
At what Time: 10:00 am
Location: Lab
H) Information Retrieval

The Information retrieval involves returning a set of
documents in response to a user query. Internet search engines use the
information retrieval system. Moreover, one can change from classical
information retrieval is that Internet searching now uses the methods
that rank the documents according to how many links there are to them
(example Google’s PageRank) as well as the presence of search terms.
I) Search Engines and Semantic Web Search:

The web search engine is a software application that is
devised to search for information on the internet (World Wide Web). The
search results are normally presented in a line of results often
referred to as search engine results pages (SERPs). Semantic Web search
engines are applications for finding ontologies that require reasonable
effort: queries are usually written as natural language keywords and
results are ranked.
J) Question Answering

It attempts to find a specific answer to a particular
question from a collection of documents, or short piece of text that
contains the answer. For example, what is the capital of India?
K) Collaborative Filtering

The technology to make recommendations based on user
behavior on an E-commerce website. From your history or previous search
e-commerce website provide us with a recommendation
Natural Language Processing in Other Fields
Apart from the above application, there are some other fields where Natural Language Processing is used which are as follows,
- Politics
- E-governance
- Bio-Medical
- Forensic Science
- Business Development
- Marketing
- Advertisement
- Education
Architecture of Natural Language Processing
The input to the Natural Language Processing system could be
speech or text. It could also be a gesture (multimodal input or perhaps
a Sign Language).
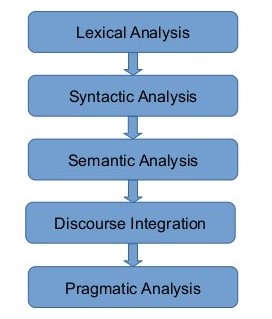
Lexical and Morphological Analysis
The lexicon of a language is its vocabulary which includes
its words and expressions. The Morphology depicts analyzing, identifying
and description of a structure of words. The lexical analysis involves
dividing a text into paragraphs, words and the sentences
Syntactic Analysis
Syntax focuses on the proper ordering of words and its
effect on meaning. This focuses on the analysis of the words in a
sentence to depict the grammatical structure of the sentence. The words
are transformed into a structure that shows how the words are related to
each other. Example, “The boys the go to the school.” This sentence
would be rejected by the English syntactic analyzer.
Semantic Analysis
Semantics focus on the meaning of words, sentences, and
phrases. This abstracts the dictionary meaning or the exact meaning from
context. The structures which are created by the syntactic analyzer are
assigned meaning Example, “colorful blue idea.” This sentence would be
rejected by the analyzer as colorful blue do not make any sense
together.
Discourse Integration
It finds out the sense of the context. The meaning of any
single sentence depends upon the sentences that precede it and also
invokes the meaning of the phrases that follow it. Example the word “it”
in the sentence “she wanted it” depends upon the prior discourse
context
Pragmatic Analysis
Pragmatics concerns the overall communicative and social
context and its effect on interpretation. It means abstracting or
deriving the purposeful use of the language in situations, importantly
those aspects of language which require world knowledge. The main focus
is on what was said is reinterpreted on what it means.
- E.g. “close the window?” should have been interpreted as a request rather than an order
Components of Natural Language Processing
The important components of Natural Language Processing are as follows
- Input Pre Processing: speech/gesture recognizer or text pre-processor
- Morphological Analysis
- Speech Tagging
- Parsing — This includes syntax and compositional semantics
- Disambiguation: It can be done as part of parsing
- Context Module: It maintains information about the context
- Text Planning: The part of language generation / what meaning to convey
- Tactical Generation: It converts meaning representations to strings.
- Morphological Generation
- Output Processing: text-to-speech, text formatting, etc.
Use of NLTK for Natural Language Processing:

Natural language toolkit i.e., NLTK is one of the most
popular libraries for natural language processing (Natural Language
Processing) and very easy to learn. It has been written in Python and
has a big community behind it.
